Neptune
Welcome to Neptune, the ultimate online platform for students! At Neptune, students can collaborate, share ideas, and utilize a suite of powerful tools to boost their productivity and excel in their studies.
Features
- Collaboration: Connect with fellow students, work together on projects, and share resources.
- Productivity Tools: Make use of various tools like Gemini to enhance your efficiency and manage your time effectively.
- Community: Join a vibrant community of motivated students who are all striving to be their best.
My Feature: Customizable Themes
Personalize the look and feel of Neptune to suit your preferences. Our customizable themes are designed to keep you engaged and focused on your work, making your experience both enjoyable and productive.
Join Neptune today and become the most productive student you can be!
Demo
Successful Postman Request
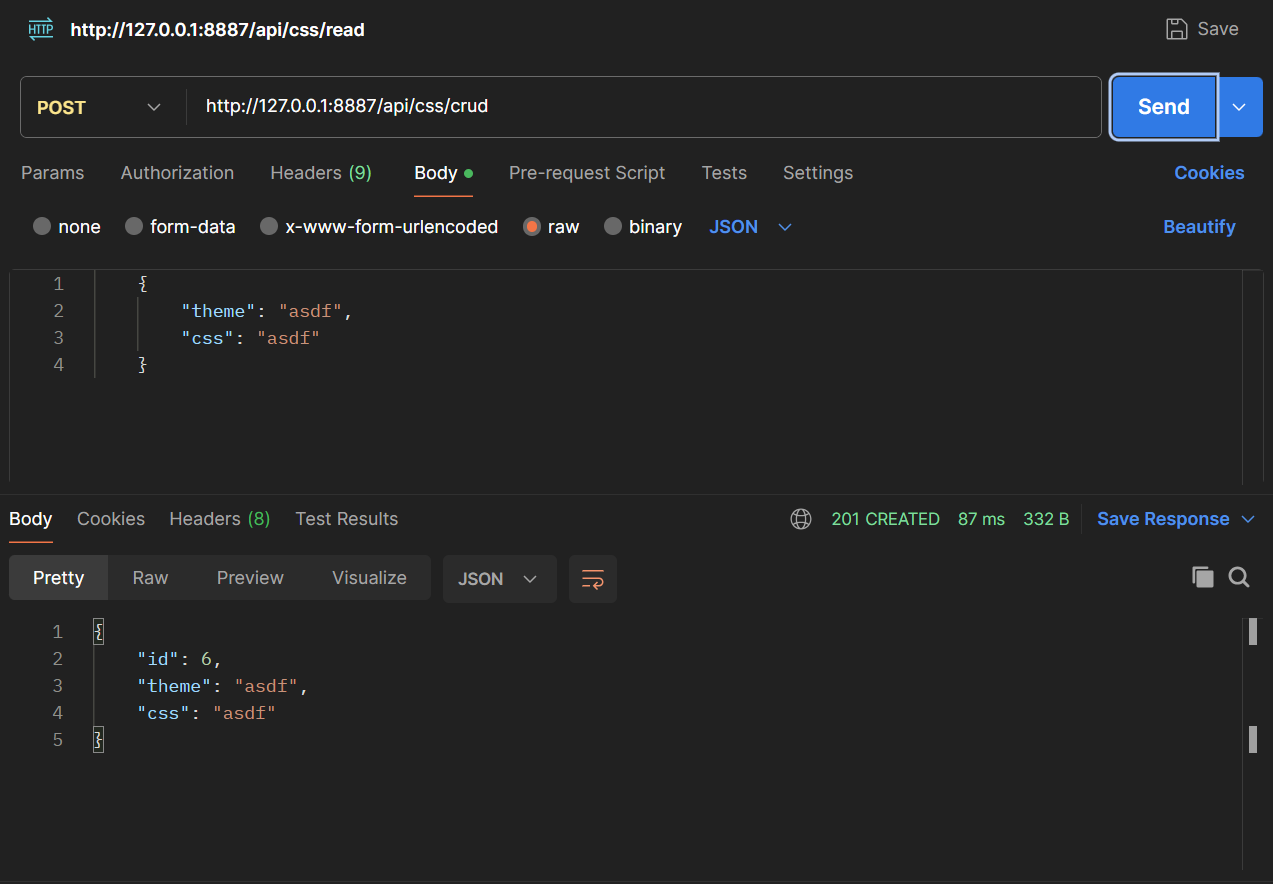
The above image shows a successful Postman request. This indicates that the API request was properly formulated and received the expected response.
Error in Postman Request
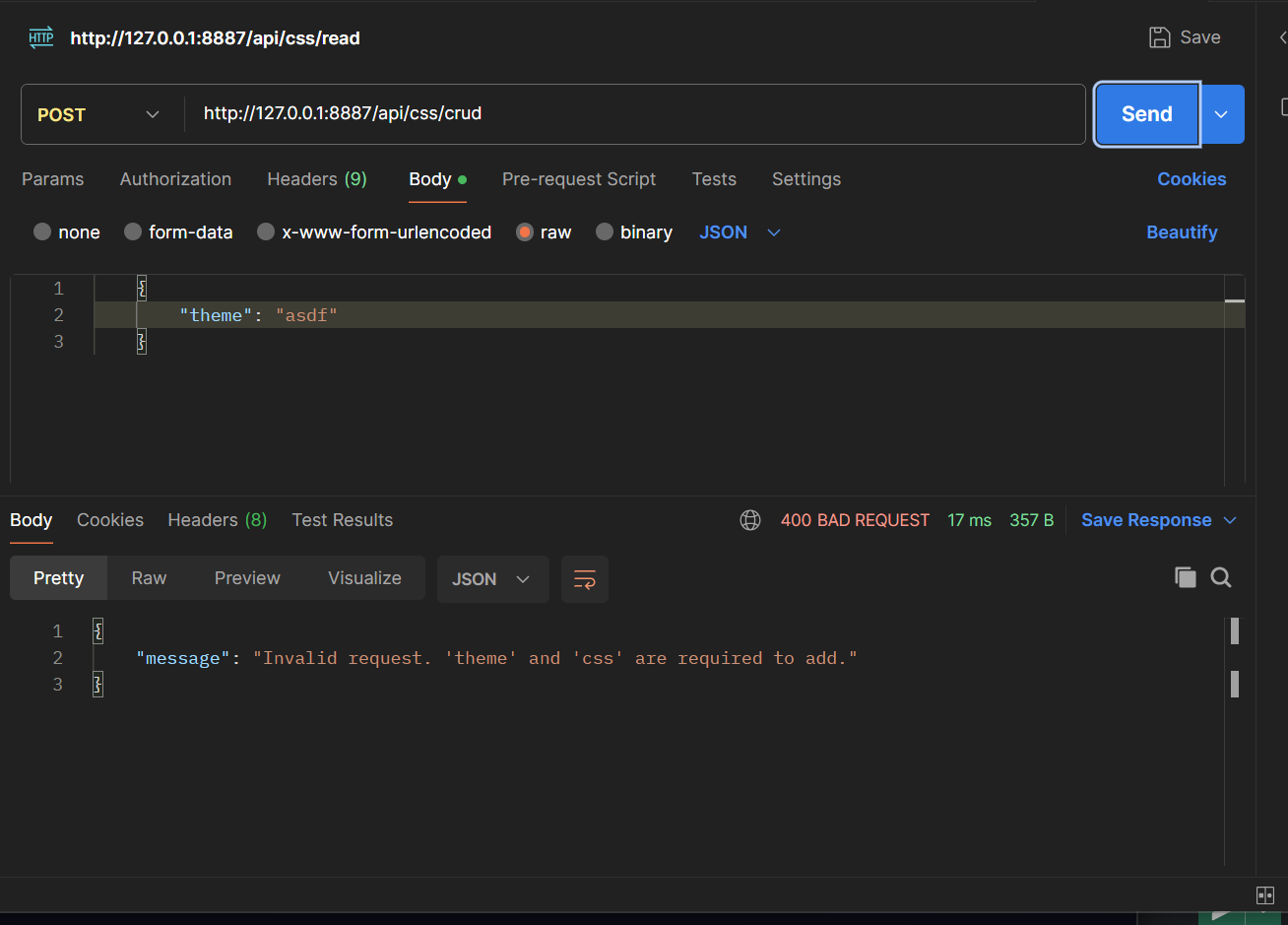
The above image displays an error that occurred due to not enough information given in the body. The theme cannot be created if a CSS isn’t given and vice versa.
Intializing the Table
The “Class” Model is defined with the code below and includes 2 key fields or columns, “_theme” and “_css”.
- “_theme” represents the name of the theme
- “_pick” represents the name/filepath of the CSS for that specific them
class Theme(db.Model):
__tablename__ = 'themes'
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
_theme = db.Column(db.String(255), unique=True, nullable=False)
_css = db.Column(db.String(255), unique=True, nullable=False)
def __init__(self, theme, css):
"""
Constructor, 1st step in object creation.
Args:
theme (str): The name of the theme.
css (str): The CSS associated with the theme.
"""
self._theme = theme
self._css = css
Initialization Function
The function named “initThemes()” is defined and will populate the table with sample data when the database is intialized
def initThemes():
with app.app_context():
"""Create database and tables"""
db.create_all()
"""Tester data for table"""
t1 = Theme(theme='Red', css="testpath1")
t2 = Theme(theme='Green', css="testpath2")
themes = [t1, t2]
for theme in themes:
try:
theme.create()
except IntegrityError:
'''fails with bad or duplicate data'''
db.session.rollback()
Create Function
The code below defines a create method named “create()” that will add a new class to the table.
def create(self):
try:
db.session.add(self)
db.session.commit()
except Exception as e:
db.session.rollback()
raise e
In the the API file named themes.py, an endpoint is defined at api/css/crud that handles post, get, put, and delete requests. It validates the user’s input ensuring that all 2 required fields have been filled out and then uses the defined create method to add the record to the table
def post(self):
try:
# Get request body
body = request.get_json()
if not body or 'theme' not in body or 'css' not in body:
return {"message": "Invalid request. 'theme' and 'css' are required to add."}, 400
theme = body['theme']
css = body['css']
# Create a new theme
new_theme = Theme(theme=theme, css=css)
new_theme.create()
# Return success response
return new_theme.read(), 201
except Exception as e:
return {"message": f"Error adding theme: {str(e)}"}, 500
Read Function
This code below in the model file defines a read method in which the it retrieves the data for a theme and returns it as a dictionary
def read(self):
return {
'id': self.id,
'theme': self._theme,
'css': self._css,
}
In the API file, the code below retrieves all the data from api/css/read by calling the defined read() function for each record. I used a post request as I needed to get the CSS for a specific theme, and not the full table, however if I need the full table, a get request is also a valid option.
def post(self):
try:
# Parse the JSON body
body = request.get_json()
# Validate the input
if not body or 'theme' not in body :
return {"message": "Invalid request. 'theme' is required to read."}, 400
theme_name = body['theme']
# Find the theme by name
read_theme = Theme.query.filter_by(_theme=theme_name).first()
if read_theme:
# Use the model's update method to handle updates
read_theme2 = read_theme.read() # Returns the full dictionary
css_value = read_theme2.get('css') # Extracts only the CSS value
if read_theme:
return {
"css":css_value}, 200
else:
return {"message": "Theme not found."}, 404
except Exception as e:
return {"message": f"Error occurred: {str(e)}"}, 500
Update Function
This code below defines the update function named “update()” that will modify the table’s data. It accepts a dictionary of inputs and updates the relevant fields, then commits the changes to the table.
def update(self, inputs):
if not isinstance(inputs, dict):
return self
theme = inputs.get("theme", "")
css = inputs.get("css", "")
# Update table with new data
if theme:
self._theme = theme
if css:
self._css = css
try:
db.session.commit()
except IntegrityError:
db.session.rollback()
return None
return self
Then in the api file, this code below uses the previously defined update function to accept incoming JSON data that contains the id of the row that the user would like to change, the new data that the user would like to change it to, and finally replace the data and commit it
def put(self):
try:
# Parse the JSON body
body = request.get_json()
# Validate the input
if not body or 'theme' not in body or 'css' not in body:
return {"message": "Invalid request. 'theme' and 'css' are required to update."}, 400
theme_name = body['theme']
new_css = body['css']
# Find the theme by name
update_theme = Theme.query.filter_by(_theme=theme_name).first()
if update_theme:
# Use the model's update method to handle updates
updated_theme = update_theme.update({'css': new_css})
if updated_theme:
return {
"message": f"Updated Theme: {theme_name} updated_theme: {updated_theme.read()}"}, 200
else:
return {"message": "Theme not found."}, 404
except Exception as e:
return {"message": f"Error occurred: {str(e)}"}, 500
def get(self):
try:
themes = Theme.query.all()
return [theme.read() for theme in themes]
except Exception as e:
return {"message": f"Error fetching themes: {str(e)}"}, 500
Delete Function
The delete functionionality is handled in the API file which uses the session.delete method which interacts with the table directly. It is pretty straightforward as the code below essentially just a delete method to api/css/crud to delete row from the table. The code searches for the theme, and removes the entire row.
def delete(self):
try:
body = request.get_json()
if not body or 'theme' not in body:
return {"message": "Invalid request. 'theme' is required to delete."}, 400
theme_name = body['theme']
# Find the theme by the provided name
del_theme = Theme.query.filter_by(_theme=theme_name).first()
if del_theme:
del_theme.delete()
return {"message": f"Deleted Theme: {theme_name}"}, 200
else:
return {"message": "Theme not found"}, 404
except Exception as e:
return {"message": f"Error unable to delete theme: {str(e)}"}, 500