Customizable Themes
Personalize the look and feel of Neptune to suit your preferences. Our customizable themes are designed to keep you engaged and focused on your work, making your experience both enjoyable and productive.
CPT Requirements Table
| CPT Requirement | Feature Embodying the Requirement | How This Feature Fulfills the Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| A List | Database stores multiple entries | The database stores and retrieves multiple programming languages as list items. |
| A Procedure | initThemes() function |
Initializes the database with test data, ensuring structured data setup. |
| A Call to the Procedure | fetchUserTheme() function |
Calls an API endpoint to fetch data from the backend. |
| Selection | Conditional checks in API routes | Ensures valid data is processed before adding/updating database entries. |
| Iteration | for loops in Python & JavaScript |
Loops iterate through database entries and frontend responses to process them. |
| Input from User | Users select their theme from the frontend | The selected theme gets saved to a template in the backend. |
Theme Selection & Application Process
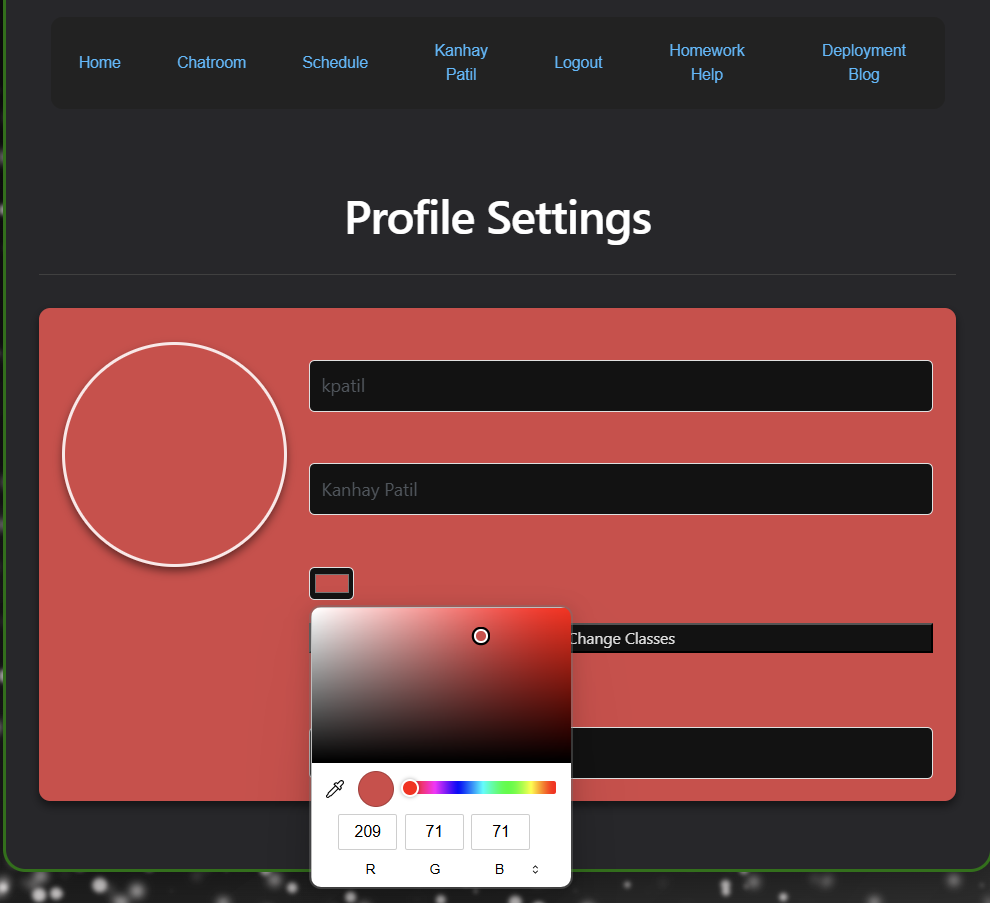
1. User Interface: Selecting a Theme Color
When a user selects a color for their theme, the frontend captures their selection and updates their theme accordingly.
Frontend UI:
2. Database Updates on User Creation
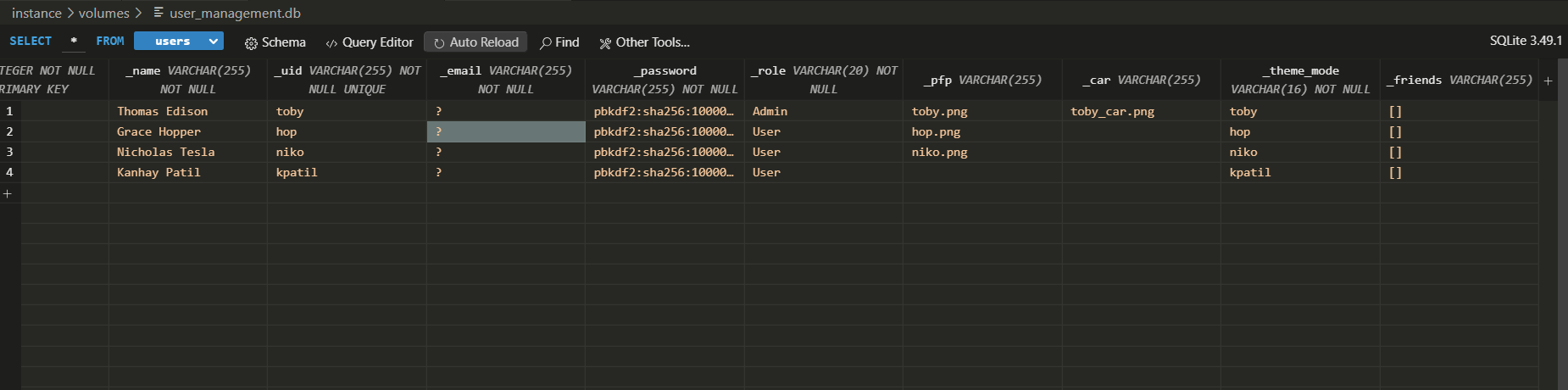
Whenever a new user is created, two things happen in the database:
- The
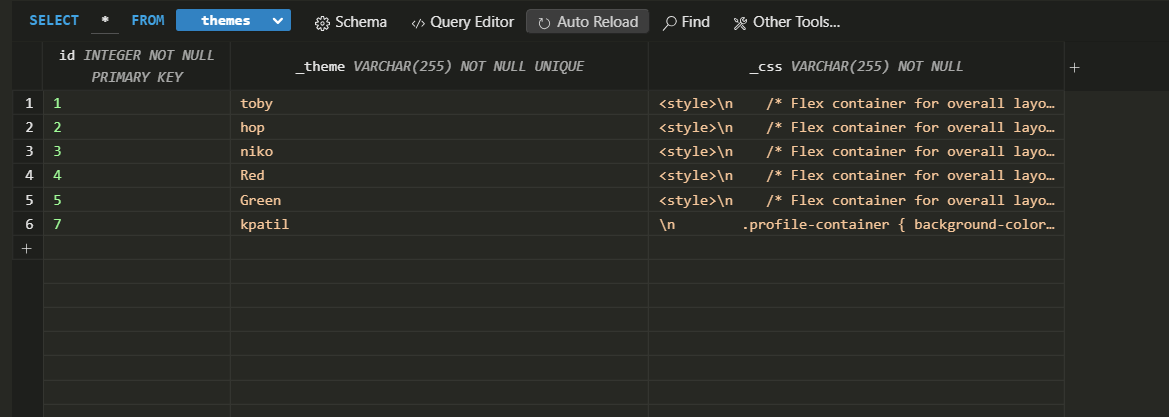
theme_modecolumn in the users table is populated with the user’s unique ID (uid). - A new row is added to the themes table with the user’s unique ID and associated CSS.
Users Table:
Themes Table:
3. Fetching the User’s Current Theme
When the user selects a new color, the frontend first determines the theme currently assigned to them.
Fetch User’s Theme
async function fetchUserTheme() {
try {
const response = await fetch(`${pythonURI}/api/user`, fetchOptions);
if (!response.ok) throw new Error(`Failed to fetch theme: ${response.status}`);
const data = await response.json();
return data.theme_mode || null;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error fetching theme:", error);
return null;
}
}
4. Updating the User’s Theme in the Backend
Once the user’s theme is identified, an update request modifies the backend with the color they selected.
Update User’s Theme Color
async function updateUserThemeColor() {
console.log("Color picker changed!");
const colorPicker = document.getElementById("themeColor");
if (!colorPicker) {
console.error("Color picker element not found!");
return;
}
const primaryColor = colorPicker.value;
console.log(`Selected Color: ${primaryColor}`);
let userTheme = await fetchUserTheme();
if (!userTheme || typeof userTheme !== "string") {
console.warn("No user theme found, creating one...");
userTheme = await createDefaultTheme(primaryColor);
}
console.log(`Updating theme: ${userTheme} with color ${primaryColor}`);
const css = generateCSS(primaryColor);
try {
const response = await fetch(`${pythonURI}/api/css/crud`, {
method: "PUT",
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" },
body: JSON.stringify({ theme: userTheme, css })
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`Failed to update theme: ${response.status}`);
}
console.log("Theme color updated successfully.");
const updatedCSS = await fetchUserCSS(userTheme);
if (updatedCSS) applyRawCSS(updatedCSS);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error updating theme color:", error);
}
}
5. Fetching the Updated Theme’s CSS
After updating the backend, a POST request retrieves the user’s theme. A POST request is used instead of GET because GET cannot have a body and would return all themes.
Fetch User’s Updated Theme CSS
async function fetchUserCSS(theme) {
try {
const response = await fetch(`${pythonURI}/api/css/read`, {
method: "POST",
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" },
body: JSON.stringify({ theme_name: theme })
});
if (!response.ok) throw new Error(`Failed to read theme: ${response.status}`);
const data = await response.json();
console.log("Fetched CSS data:", data);
return data.css || null;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error fetching theme CSS:", error);
return null;
}
}
6. Applying the Updated CSS to the Frontend
Once the updated CSS is retrieved, it is dynamically applied to the user interface.
Generate and Apply CSS
function generateCSS(primaryColor) {
return `
.profile-container { background-color: ${primaryColor}; }
#profileImageBox { border: 4px solid ${primaryColor}; }
.file-icon, label, input { color: ${primaryColor}; border-color: ${primaryColor}; }
#applytheme, .side-btn { background-color: ${primaryColor}; }
#applytheme:hover, .side-btn:hover { background-color: ${adjustColor(primaryColor, -10)}; }
`;
}